Understanding CT Scans for Lung Cancer: A Comprehensive Guide
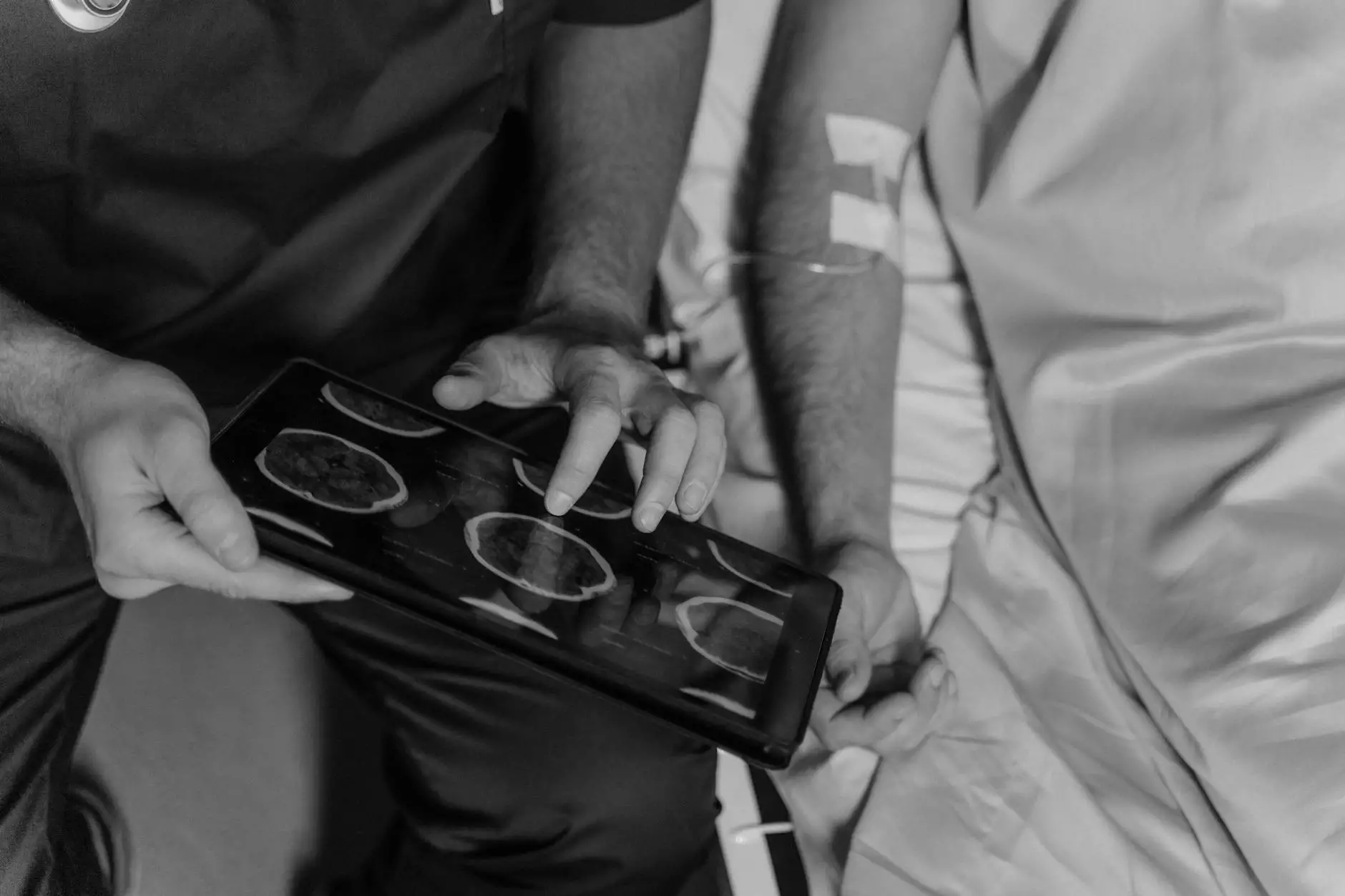
In today's modern medical landscape, diagnostics play a crucial role in effective treatment planning. Among the various diagnostic tools available, the CT scan for lung cancer stands out as a powerful method for detecting and assessing lung cancer. This article dives deep into the world of CT scans, their significance in lung cancer diagnosis, the procedures involved, and the broader context of respiratory health.
What is a CT Scan?
A CT scan, or computed tomography scan, is a detailed imaging technique that combines X-ray images taken from different angles and uses computer processing to create cross-sectional images of bones, blood vessels, and soft tissues inside the body. CT scans provide more detailed information than standard X-rays and are particularly useful in oncology for identifying cancerous tissues.
Why is a CT Scan Used for Lung Cancer?
The CT scan for lung cancer is an essential tool that serves multiple purposes:
- Early Detection: CT scans can identify lung tumors at an early stage, which is critical for improving survival rates.
- Diagnosis Confirmation: They help confirm the presence of lung cancer after initial tests, such as chest X-rays.
- Staging of Cancer: CT scans are used to determine the size of the tumor and whether it has spread to nearby lymph nodes or other organs.
- Guidance for Treatment: They assist doctors in developing targeted treatment plans, including surgery, radiation therapy, or chemotherapy.
The CT Scan Procedure
Preparation for the Scan
Preparation for a CT scan is generally straightforward. Patients may need to:
- Avoid eating or drinking for a few hours before the scan, especially if contrast dye will be used.
- Inform the healthcare provider about any allergies, particularly to iodine or contrast materials.
- Wear loose clothing and remove any metal items that may interfere with imaging.
During the Scan
The actual CT scan procedure lasts only a few minutes:
- Patients lie on a table that slides into the CT scanner, which looks like a large donut.
- The scanner rotates around the patient, capturing multiple images from various angles.
- In some cases, patients may receive a contrast material through an intravenous (IV) line to enhance image quality.
- Patients must remain still and may be asked to hold their breath for short periods during the scan.
After the Scan
After the procedure, patients can usually resume normal activities immediately. If contrast dye was used, hydration is often encouraged to help flush it from the body.
Benefits of CT Scans in Lung Cancer Diagnosis
The advantages of using CT scans for lung cancer are numerous:
- High Sensitivity: CT scans can detect tumors that may not be visible through other methods.
- Non-Invasive Procedure: Unlike surgical biopsies, CT scans are quick and do not involve any invasive procedures.
- Comprehensive Information: They provide detailed images that help in understanding tumor characteristics, size, and location.
- Monitoring Progress: CT scans can monitor the effectiveness of treatment strategies over time.
Risks and Considerations
While CT scans are generally safe, there are some factors to consider:
- Radiation Exposure: CT scans expose patients to more radiation than standard X-rays, which may slightly increase cancer risk. However, the diagnostic benefits often outweigh the risks.
- Allergic Reactions: Some patients may experience allergic reactions to contrast dye, although these are rare.
- Inconclusive Results: Although CT scans are effective, they can sometimes yield inconclusive results that necessitate further testing.
Understanding Lung Cancer Staging
A CT scan for lung cancer is vital for accurate staging, which influences treatment decisions:
Stage 0 (Carcinoma in Situ)
At this stage, abnormal cells are present but have not invaded nearby tissues.
Stage I
The cancer is localized in the lungs and has not spread to nearby lymph nodes or distant sites.
Stage II
Cancer has spread to nearby lymph nodes or deeper into lung tissues but is still contained.
Stage III
The disease is more extensive, indicating invasion into surrounding tissues or more distant lymph nodes.
Stage IV
This stage signifies metastatic cancer, where the disease has spread to other organs or distant sites.
Advancements in CT Technology
Recent advancements in CT technology continue to improve the accuracy and safety of lung cancer diagnostics:
- Low-Dose CT Scans: These scans use lower radiation doses, making lung cancer screenings safer, especially for high-risk patients.
- 3D Imaging: Advances allow for three-dimensional reconstructions, enhancing visualization of complex structures.
- AI Integration: Artificial intelligence is increasingly used in analyzing CT images to assist radiologists in detecting abnormalities.
Conclusion: The Role of CT Scans in Lung Cancer Management
In conclusion, the CT scan for lung cancer is a crucial component of modern oncology, enabling early detection, accurate diagnosis, and effective treatment planning. Increased awareness and understanding of this diagnostic tool can empower patients to seek necessary screenings and contribute to improved health outcomes. At Hello Physio, we prioritize patient education and holistic health, offering supportive resources for lung cancer patients and their families.
Always consult with healthcare professionals regarding lung health and the role of diagnostic scans in managing respiratory conditions. With insightful knowledge and timely intervention, we can navigate the complexities of lung cancer and enhance the quality of life for those affected.
Resources and Further Reading
For more information on lung cancer and diagnostics, consider exploring the following resources:
- American Cancer Society - Lung Cancer
- American Lung Association - Lung Cancer
- National Center for Biotechnology Information - CT Lung Cancer Screening









